
Before logical block addressing (LBA) were introduced, the active, primary partition could not exceed 7.8 GB, regardless of the file system used. The calculation results in a maximum capacity of slightly less than 8 gigabytes ( GB).
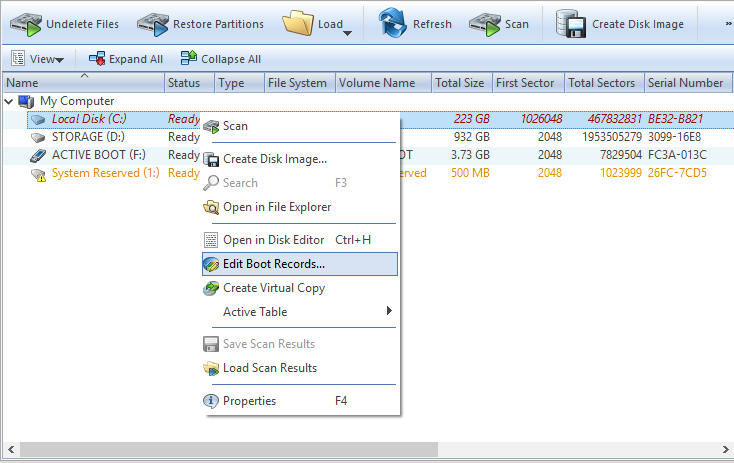
Maximum capacity = sector size x cylinders (10 bits) x heads (8 bits) x sectors per track (6 bits) However, the enumeration of sectors starts at 1 (not 0, as for other fields), so the maximum number of sectors per track is 63.īecause all hard disks are low-level formatted with a standard 512-byte sector, the maximum disk capacity described by the partition table is calculated as follows: Right-click the MBR disk that you want to change into a GPT disk, and then click Convert to GPT Disk. If the disk contains any partitions or volumes, right-click each and then click Delete Partition or Delete Volume. The Starting Sector and Ending Sector fields are each six bits long, which limits the range of these fields to 0–63. Back up or move the data on the basic MBR disk you want to convert into a GPT disk. The Starting Head and Ending Head fields are each one byte long, which limits the field range to 0–255. The Ending Cylinder field in the partition table is 10 bits long, which limits the number of cylinders that can be described in the partition table to a range of 0–1,023. If your disk fails, you need to work with the partition starting point (among other factors) to retrieve stored data. Knowing the starting sector of an extended partition is very important for low-level disk troubleshooting. It identifies how and where the systems operating. Once you’ve started Command Prompt on your problem computer, you can use some advanced tools in it to repair the boot records. The Starting CHS fields for non-active partitions point to the boot sectors of the remaining primary partitions and the EBR of the first logical drive in the extended partition. The Master Boot Record (MBR) is the information in the first sector of a hard disk or a removable drive. Use Command Prompt to fix issues with your PC’s boot records. You can use, for example, the Disk Probe program on Windows NT Workstation Resource Kit CD to display the Master Boot Record, and compare it to the Master Boot Record. The master boot code uses these fields to find and load the boot sector of the active partition. Because the code in the Master Boot Record executes before any operating system is started, no operating system can detect or recover from corruption of the Master Boot Record. These fields are essential for starting the computer.
The Starting and Ending chs (Cylinder, Head and Sector) fields are additional elements of the partition table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
